The purpose of the Gilbert’s behavior engineering model is to improve performance by determining the influences that affect behavior as well as the methods of modifying behavior.
The model uses six conditions of behavior to promote performance improvement, and requires that all six conditions be present for performance improvement to occur:
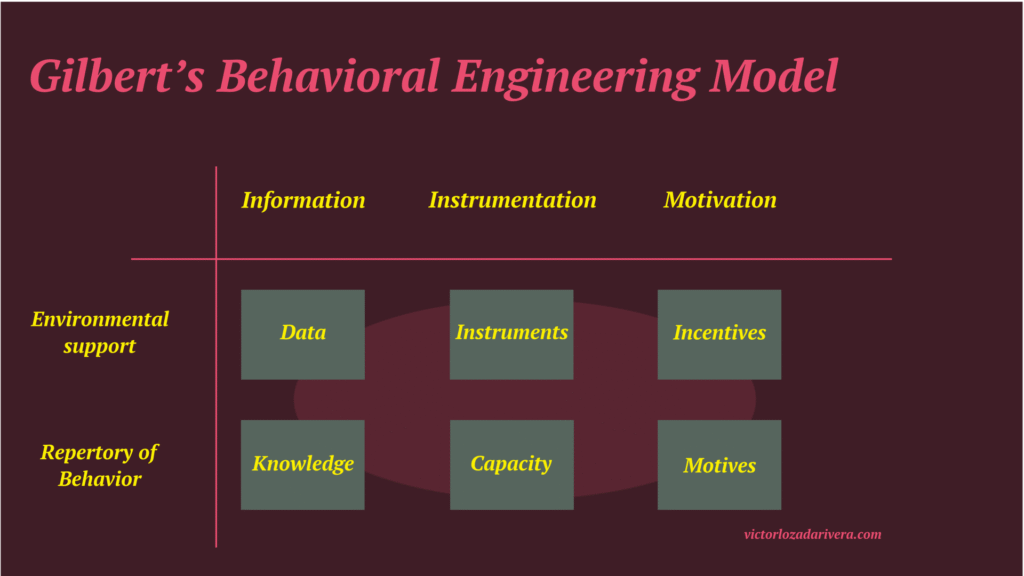
Environmental support
The first element of the BEM is environmental support which focuses on three components: data (information), resources (instrumentation), and incentives (motivation)
- Data, focuses on expectations and feedback. Duties cannot be expected to be done adequately without clearly understanding the expectations including the conditions to perform the duties.
Expectation and feedback must be relevant and frequent in order to produce adequate performance of the task or duty. However, it cannot be so frequent that information overload occurs.
- Instruments, includes the resources designed to match human elements. These instruments, both psychological and physiological, are the materials, tools, and time needed to accomplish tasks including clearly defined processes and procedures.
Behavior cannot assess the performance of a duty and provide meaningful feedback if the individuals are not provided with the necessary resources.
- Incentives, includes the consequences and encouragements for performance improvement. The purpose of the incentives is to motivate improvement in performance over both the short and the long term.
Repertory of Behavior
The second element of BEM focuses is repertory of behavior on three components: the knowledge (information), response capacity (instrumentation), and motives (motivation) for creating competence.
- Knowledge, focuses on the knowledge and skills needed to perform task adequately. Feedback must be effective and meaningful to ensure that duties are adequately performed or to provide additional training to bring the knowledge and skills level up to par.
- Capacity, focuses on the unique experiences the learner brings. These include, social skills, personal qualities, and past experiences.
- Motives, surrounds the motives and preferences, specifically satisfaction of the performer. Performers’ satisfaction includes attitudes towards the job including personal preference for the position, available incentives, and environmental factors
Conclusion
Gilbert explains that behavior is a result of the environmental support and the behavior repertory of individuals. Instructors can optimize behavior by providing the appropriate information, instrumentation, and motivation to support the environment and the behavioral repertory.
Need to motivate a learner or creating a better learning environment? Check out ARCS Motivational Model and Components of Cognitive Apprenticeship, respectively.
Are you a manager, instructor, or teacher? Tell me in the comments how this model applies to your field.


