When a learning resource is meant to be taught by other instructors, the developer must provide the information that will allow others to use the resource as intended. A clearly written facilitator guide becomes an essential element of sharable educational materials.
In this ultimate guide I will go through the 15 components needed to create a facilitator guide for your educational material.
- Overview
- Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- How to Use the Facilitator Guide
- Course Description
- Purpose, Goals, and Objectives
- Intended Audience
- Prerequisites
- Instructor Qualifications and Responsibilities
- Required Resources
- Procedures and Strategies for Implementation
- Assessment
- Relationship to Other Educational Materials
- Extension Activities
- List of References
Let’s begin!
Cover Page
Provide a cover with a title for your educational resource. Credit yourself, if you are the author and other involved (other contributors, funding agencies, etc). List all important contact information such as email, mailing address, phone number, and include the date the material was developed.
Table of Contents
A table of contents is an important overview of the material, this is especially important for guides longer than 10 pages.
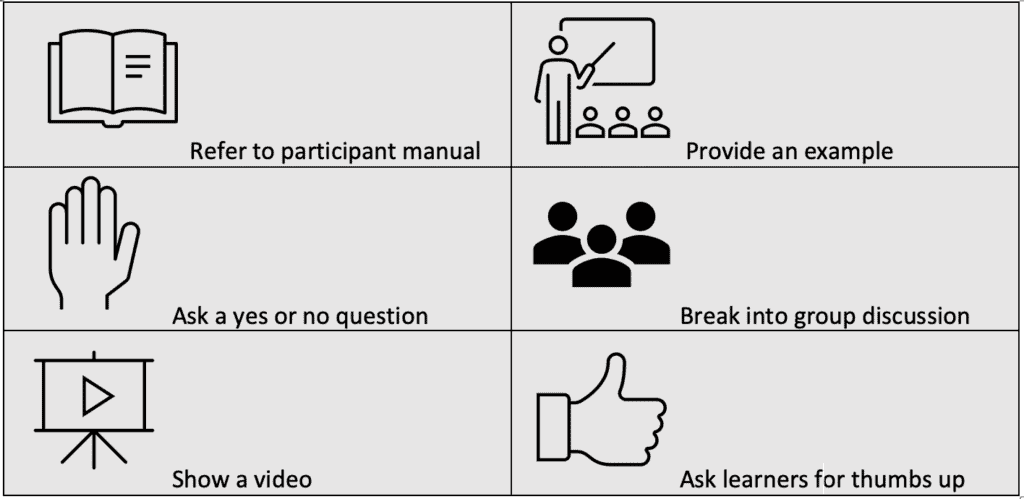
How to Use the Facilitator Guide
Facilitator guides are often full of icons and pictures that indicate to the instructor specific actions. Here is where you would include a chart or diagram with your icons and their respective descriptions.
EXAMPLE:
Course Description
Think of this as an introduction to the course but from an instructors point of view. Summarize the main idea behind the course and describe the key elements. This course description is equivalent to the abstract you find in academic journals. It serves as the snapshot of the course, so instructors can determine if your resource suits their needs.
EXAMPLE:
“This 1 hour virtual instructor led course is designed to provide Wellness Services client service professionals with an overview and demonstration of the BMI calculator tool. By the end of this training, participants will be better able to recognize how the tool’s functionality may be beneficial, and engage those potential clients in an informative dialogue concerning the benefits and key features of the tool.”
Purpose, Goals, and Objectives
Provide a brief description of the purpose of the course and the course goals or learning objectives. This information helps instructors and learners place the material into the context of other curricular activities with related goals or objectives.
EXAMPLE:
By the end of this course, participants should be better able to:
• Identify the profile of prospective clients
• Articulate the benefits and key features of the tool to prospective clients
• Demonstrate how the tool helps meet prospective client needs
Intended Audience
Describe your intended audience. Clearly state the level of learner for which this educational resource is relevant and for those it is not. Curriculum designers and instructors can quickly determine the appropriateness of a particular educational resource for their target audience.
EXAMPLE:
“The workshop is intended for medical students and students from other health-care disciplines who have little or no knowledge, experience, or skill in BMI. The workshop is not intended for those who already have knowledge and experience assessing the cognitive functioning of older adults. This is a beginning program — a workshop focusing on the basics of BMI.”
Prerequisites
For teaching or assessment resources, learners may be expected to have completed prerequisite training or have familiarity with certain terms or content. Include in this section any assumptions about the preparedness of the learner. Include prerequisite knowledge, skills, and attitudes in this section or as an extension to the intended audience section
EXAMPLE:
“Before completing an online self-assessment of knowledge about diet and nutrition, the learner may first need to complete a training module on exercise. Alternatively, an advanced computer-assisted module on assessment of proper diet and nutrition may require that participants have a basic understanding of diet and of nutrition assessment.”
Instructor Qualifications and Responsibilities
When materials are developed for a specific discipline or when they contain complex information, the instructor may need specific experience in order to establish credibility with the intended audience and to address their questions.
Other times, certain presentation, language, or software skills may be preferred, because they increase the likelihood that the educational resource will be implemented successfully. Instructors must be capable in administering the assessment tools and methods.
Include in this section any special recommendations for the instructors regarding the course and/or the course materials.
EXAMPLE:
Instructors should have adequate grasp of food science and biology. Instructors may need to remind the learners that they should review the material from last week’s training.
SPECIAL NOTICE: This is a 1-hour VILT (Virtual Instructor-Led Training) Make sure you take a break at 30-minutes!
Required Resources
Provide a list of all equipment need to set up the class (tables, projector, open space, computer) and materials needed to administer the course (supplies, teaching aids, PowerPoints, writing material) Describe the space/room requirements and suggested set-up.
EXAMPLE:
In order to complete this course as intended, instructor will need:
• Activity worksheets
• Case descriptions
• Articles
• Notepads
• Hard copies of slides
• (optional) Annotated version of the handouts
A Learner’s guide sometimes may be included in the course. The manual may be relevant for self-guided learning module as well as workshops. If a Learner’s guide is available to the learners, the instructor must be familiar with the content and able to refer to it during the session.
For e-learning materials, include specific system requirements, both hardware and software, as well as any technical instruction such as basic navigation features and help systems.
Procedures and Strategies for Implementation
This is the bulk of your facilitator’s guide. In this section you need to describe step by step how to implement the course and to achieve the stated goals and objectives. Throughout this section you should use icons already specified, to offer suggestions on any given part of the course Include enough thorough details, items that might need clarification, or highlights of important elements so that instructors can know which items deserve the most emphasis.
Along with the content, it is important to explain the activity that accompanies the lesson (discussion, role-play, hands-on, cooperative learning, practice exercises, video, assessment, debriefing, feedback), the suggested order of activities, the procedures for implementation, and the estimated time for each activity.
Include suggestions regarding strategies for successful implementation.
EXAMPLE:
During this role-play session designed for up to 8 participants, it is recommended that the groups be broken into smaller groups of 4-6 participants.
Take 10 minutes to allow learners to discuss and come up with a complete thought. It is okay if this sections runs over time but cap the discussion at 15 minutes.
Having the entire group sit in big circle during the debrief sections is recommended for the entirety of the course.
To make sure that you have provided enough details in this section, consider asking someone who is totally unfamiliar with the resource to read the manual in draft. Is there anything your reader does not understand? If so, clarify before completing the final version.
Assessment
You have designed your course for a specific purpose or to meet certain learning objectives. The assessment plan is simply a description of how the instructor might determine whether the learning objectives have been achieved. Clearly, the assessment must be linked to the specific knowledge, skills, and attitudes that were incorporated in the objectives.
Consider appending any accompanying assessment tool (rating scales, MCQ questions, checklists, etc.). In e-learning materials, assessment of the learning objectives is often built into the teaching sequence. In other cases, the assessment is more informal (e.g., faculty observation of student role-playing communication skills). Regardless, specify clearly how the assessment can be accomplished.
Relationship to Other Educational Materials
Your educational course may be part of a multipart series. The current lecture may be one component of a broader program on a certain topic. A online training resource may be designed so that it is best used as part of a blended-learning strategy that also incorporates instructor-led learning elements.
Furthermore, an assessment tool can be linked to specific teaching materials, and evaluation tools can be linked to both teaching and assessment materials. Providing links to related educational resources will enable users to build a more cohesive and integrated curriculum for their target audiences.
Extension Activities
Include in this section supplemental materials, independent study suggestions, follow-up activities, or homework assignments related to the educational resource. Include some supplemental materials that allow instructors to tailor the resource to their own needs.
EXAMPLE:
Included below are websites that can be used as additional in class resources for extra allotted time or if the course run time ended earlier.
• www.biologyandmybody.com/understandingBMI
• www.nationalgeographic.com/dietsaroundtheworld
• www.BMI.com/bmicalculator .comIt is recommended to assign reading page 59-64 of the “Biology and Me” textbook to reinforce the learner’s understanding of today’s
Additionally, listed below are YouTube videos that can used as supplemental learning:
• Youtube.com/uuuiiiyyy
• Youtube.com/qqww22
• Youtube.com/0099oo
List of References
List the resources/references you used to put together the educational resource. You may also include a list of suggested further readings for the instructor or the learner.
Peer Feedback Form
Since your facilitators guide is being used by other instructor, you should consider a mechanism for feedback that will allow instructors to share their experiences with you.
Feedback is the number one way you can determine the usefulness of your course and guide. It can help you decide what changes need to be made. User reviews also are a powerful way to show social proof, that your resource is being used successfully by others.



